BP management refers to a series of methods and measures used to monitor, control, and adjust BP in order to maintain it within the normal range and reduce the risk of hypertension(HTN) and its complications.
I. Importance of BP Management
HTN is a common chronic disease that, if not effectively controlled for a long time, can cause serious damage to vital organs such as the heart, brain, and kidneys, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases like coronary artery disease and stroke. Therefore, BP management is crucial for maintaining good health.
II. Methods of BP Management
1.Monitoring BP
Regularly measuring BP:
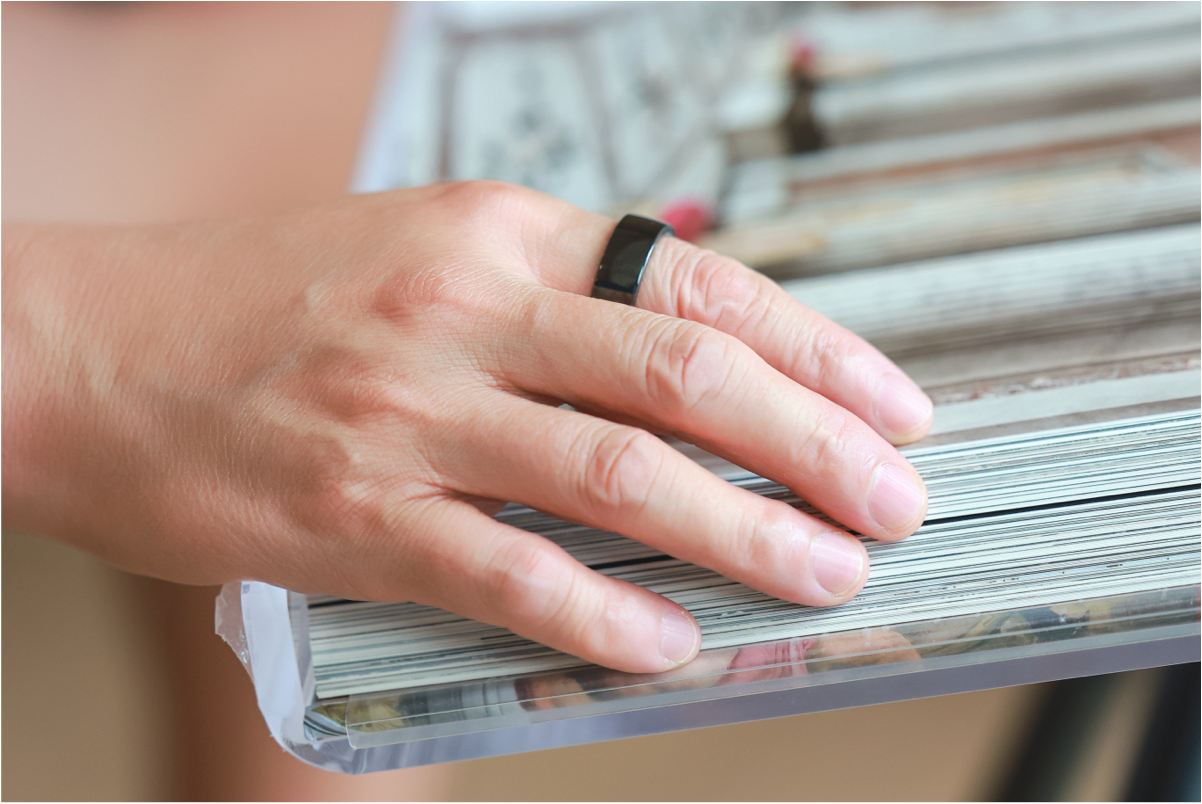
Home electronic BP monitors can be used for self-measurement, or regular measurements can be taken at hospitals or community health service centers.
Recording BP values:
Record each measurement's BP value, including the time, systolic blood pressure(SBP), and diastolic pressure, to understand the trend of BP changes.

2.Healthy Lifestyle
Reasonable diet:
Reduce sodium intake and increase potassium intake (e.g., by eating more fresh vegetables, fruits, and legumes); control fat intake, especially saturated fats and trans fats; consume protein in moderation.
Moderate exercise:
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, etc.; strength training can also be combined, e.g., weightlifting and push-ups.
Controlling weight:
Maintain a reasonable weight to avoid obesity through proper diet and moderate exercise.
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption:
Smoking raises BP and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; excessive alcohol consumption also has adverse effects on BP.
Reducing mental stress:
Maintain a positive attitude and avoid excessive tension, anxiety, anger, etc. Stress can be relieved through meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, etc.

3.Drug Therapy
a. If lifestyle interventions fail to effectively control BP, doctors may prescribe antihypertensive medications based on patients' specific conditions.
b. Patients should strictly follow doctors' advice when taking medication and not increase or decrease dosages or stop taking medication without authorization.
III. Goals of BP Management
Generally speaking, the goal of BP management is to keep BP within the normal range. For most adults, SBP should be below 120 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure below 80 mmHg. For patients with diabetes, kidney disease, and other conditions, stricter targets may apply for BP control.

IV. Precautions for BP Management
1.Accurate BP measurement:
Use correct measurement methods and equipment to ensure accurate results.
2.Persistent long-term management:
BP management is a long-term process requiring patients to consistently take action.Wearing the RING X is a simple and convenient choice, especially for those who need to monitor their BP.
3.Regular check-ups:
Patients should regularly visit hospitals or community health service centers for check-ups so that doctors can adjust treatment plans according to BP changes.
4.Pay attention to drug side effects:
Antihypertensive medications may produce some side effects such as dizziness, weakness, dry cough, etc. If side effects occur, inform your doctor promptly so they can adjust the medication accordingly.




Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.